There are four common covalent network solids: pure Carbon (C), pure Silicon (Si), Silicon carbide (SiC), and quartz (SiO2). These can all come in different combinations and shapes.
For example, Carbon is usually found in one of three forms: graphite, diamond or a buckyball (sphere-like) form. These are shown in the graphic below.
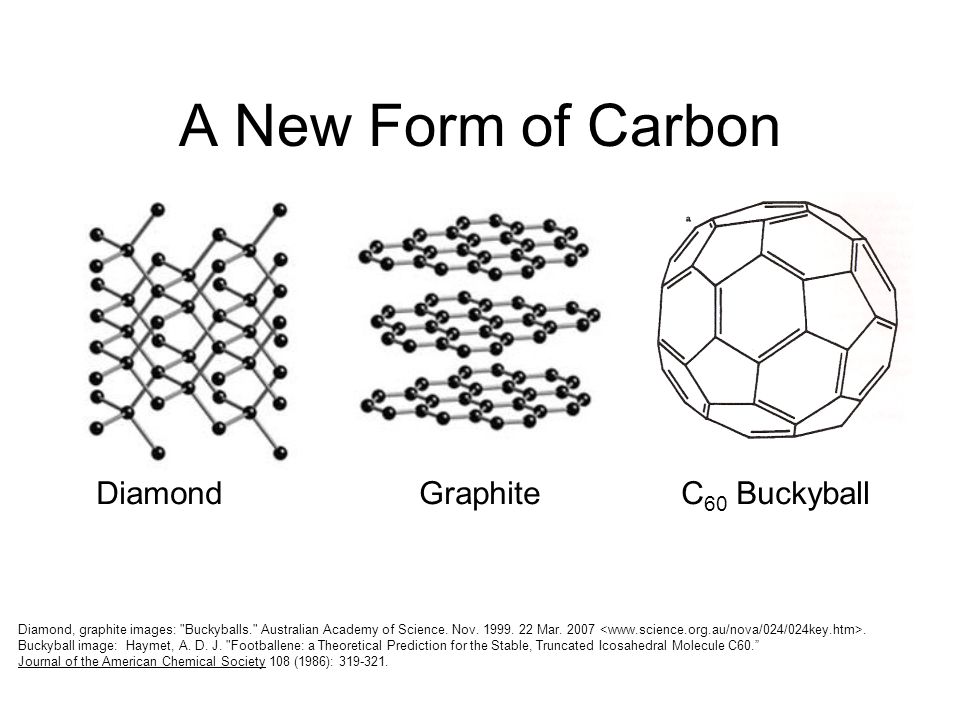 |
| Source |
| The properties of the different forms are also impacted by the different types of bonds present between its parts. For example, the color of the two different forms of carbon is impacted by the type of bonds present in them. Graphite contains alternating double bonds (w/ a pi bond) which support its parallel layering structure. These cause delocalized electrons to naturally arise which can absorb the light, which causes the black color. Diamond on the other hand contains no delocalized electrons and therefore appears white. Source |
Source:
https://chem.libretexts.org/Textbook_Maps/General_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Map%3A_General_Chemistry_(Petrucci_et_al.)/12%3A_Intermolecular_Forces%3A_Liquids_And_Solids/12.5%3A_Network_Covalent_Solids_and_Ionic_Solids
Thanks for providing recent updates regarding the concern, I look forward to read more.
ReplyDeleteThank u
ReplyDeleteAs small businesses expand, their IT needs evolve. IT support services offer scalable solutions that grow with the business. Whether it's upgrading infrastructure, integrating new software, or expanding network capabilities, it support for small businesses managed IT providers ensure that technology adapts to changing requirements, supporting sustainable growth and operational efficiency.
ReplyDeleteAt the new site, prepare the foundation according to local building codes. This foundation must be level and environmental benefits of donating a mobile home sturdy enough to support the home. Proper foundation work is essential for the home’s long-term stability.
ReplyDeleteUse-of-force training covers appropriate levels of physical intervention. Guards understand legal and top security companies in miami ethical boundaries for restraining suspects or protecting property. This training minimizes unnecessary violence and promotes accountability.
ReplyDeleteEco-conscious homeowners benefit from regular evaluations to detect water inefficiencies. Leaky faucets, toilets, and plumbing drain pipe for washing machine fixtures contribute to significant water loss. Fixing these issues early reduces your environmental footprint and lowers utility bills.
ReplyDelete